Beavers are engineering a new Alaskan tundra
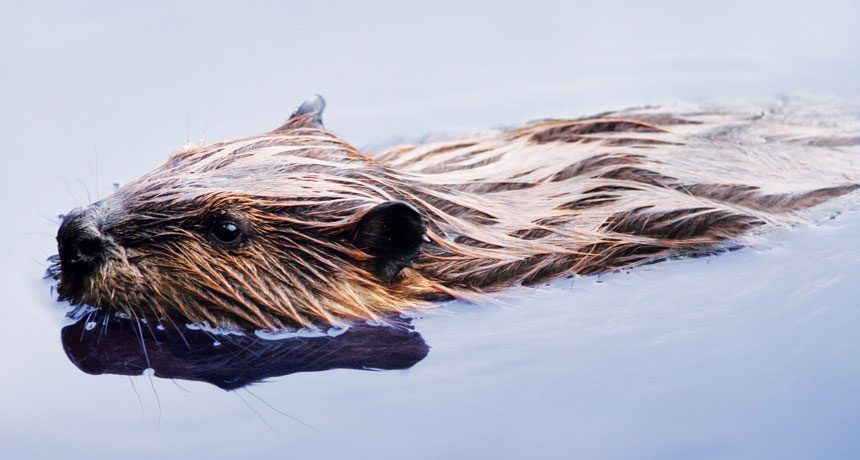

In a broad swath of northwestern Alaska, small groups of recent immigrants are hard at work. Like many residents of this remote area, they’re living off the land. But these industrious foreigners are neither prospecting for gold nor trapping animals for their pelts. In fact, their own luxurious fur was once a hot commodity. Say hello to Castor canadensis, the American beaver.
Much like humans, beavers can have an oversized effect on the landscape (SN: 8/4/18, p. 28). People who live near beaver habitat complain of downed trees and flooded land. But in areas populated mostly by critters, the effects can be positive. Beaver dams broaden and deepen small streams, forming new ponds and warming up local waters. Those beaver-built enhancements create or expand habitats hospitable to many other species — one of the main reasons that researchers refer to beavers as ecosystem engineers.
Beavers’ tireless toils — to erect lodges that provide a measure of security against land-based predators and to build a larder of limbs, bark and other vegetation to tide them over until spring thaw — benefit the wildlife community.
A couple of decades ago, the dam-building rodents were hard to find in northwestern Alaska. “There’s a lot of beaver around here now, a lot of lodges and dams,” says Robert Kirk, a long-time resident of Noatak, Alaska — ground zero for much of the recent beaver expansion. His village of less than 600 people is the only human population center in the Noatak River watershed.
Beavers may be infiltrating the region for the first time in recent history as climate change makes conditions more hospitable, says Ken Tape, an ecologist at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. Or maybe the expansion is a rebound after trapping reduced beaver numbers to imperceptible levels in the early 1900s, he says. Nobody knows for sure.
And the full range of changes the rodents are generating in their new Arctic ecosystems hasn’t been studied in detail. But from what Tape and a few other researchers can tell so far, the effects could be profound, and most of them will probably be beneficial for other species.
In the areas newly colonized by beavers, “some really interesting processes are unfolding,” says John Benson, a wildlife ecologist at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln who studies wolves and coyotes, among other beaver predators. “I’d expect some pretty dramatic changes to the areas they take over.”
Beavers’ biggest effects on Arctic ecosystems may come from the added biodiversity within the ponds they create, says James Roth, an ecologist at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, Canada. These “oases on the tundra” will not only provide permanent habitat for fish and amphibians, they’ll serve as seasonal stopover spots for migratory waterfowl. Physical changes to the environment could be just as dramatic, thawing permafrost decades faster than climate change alone would.
The Arctic tundra isn’t the first place beavers have made their mark. Changes seen in beaver-rich areas at lower latitudes may offer some clues to the future of the Alaskan tundra, home to moose, caribou and snowshoe hares.
North through Alaska
As Earth’s climate has warmed in recent years, some plants and animals — such as the mountain-dwelling pika, a small mammal related to rabbits — have fled the heat by moving to higher altitudes (SN: 6/30/12, p. 16). Others, from moose and snowshoe hares to bull sharks and bottlenosed dolphins, have moved toward the poles to take advantage of newly hospitable ecosystems (SN: 5/26/18, p. 9).
Arctic environments have changed more than most, Tape says. Polar regions are warming much faster than other parts of the world, he says. Studies estimate that average temperatures in the Arctic have risen about 1.8 degrees Celsius since 1900, about 60 percent faster than the Northern Hemisphere as a whole.
This warming is bringing great change to the Alaskan tundra, Tape says. Winter snow cover doesn’t persist as long as it used to. Streams freeze later in the fall and melt earlier in the spring. Permafrost, the perennially frozen ground, is thawing, allowing shrubs to take hold. New species are moving in, few more noticeable than the beaver. The dams they build and the ponds they create are hard to miss; these newly formed bodies of water even show up on satellite images.
Beavers have infiltrated three watersheds in northwestern Alaska in the last couple of decades. Together these drainages cover more than 18,000 square kilometers — an area larger than Connecticut.
On images of the region collected by Landsat satellites in summer months from 1999 through 2014, Tape and colleagues looked for new areas of wetness that covered at least half a hectare (1.24 acres), or about four times the area covered by an Olympic swimming pool.
The researchers then used newer, high-resolution satellite images to verify the presence of beaver ponds. Available aerial photographs taken before 1999 didn’t pick up any signs of beaver activity in the area, Tape says. Kirk notes that beavers were present in the Lower Noatak River watershed before 1999, but in vastly smaller numbers than they are today.
Based on the images at hand, the researchers found 56 new complexes of beaver ponds in the area over the 16-year study period. On average, beavers expanded their range about 8 kilometers per year, Tape and colleagues reported in the October Global Change Biology.
“This is remarkable, but it shouldn’t come as a surprise,” Tape says. “Beavers are engineers that work every day, all summer long.”
The animals have also made their way into western Alaska’s Seward Peninsula and the northern foothills of the Brooks Range, mountains that stretch east to west across northern Alaska, the researchers found. If the animals’ recent rate of expansion continues, beavers could spread throughout Alaska’s North Slope in the next 20 to 40 years, the researchers say.
The Lower Noatak River watershed, one of the areas that Tape and colleagues studied, is mostly tundra. By definition that means treeless plain. But the area also is about 3.5 percent forest, mainly concentrated along the river and its tributaries. The watersheds just to the north are completely tundra. So how do the beavers there build dams without trees? In those areas, Tape says, the animals construct smaller dams than they might at lower latitudes, using the branches, twigs and foliage of willows and other shrubs.
“I never expected to see beavers on the tundra,” Roth says, intrigued by Tape’s team’s findings.
Happy place
The beavers are not only persisting on the tundra, they’re thriving. The moderately sized streams and flat terrain provide ideal habitat. And once they gain a foothold, these industrious creatures set about making improvements that are probably an overall plus for myriad other species, Tape says.
For instance, frigid conditions in the region cause shallow streams to freeze solid in winter. But when a beaver builds a dam, the water that gathers upstream of the structure becomes deep enough to remain liquid below a sheet of ice that provides insulation from the chilly winter air.
That persistent liquid lets the beavers move about under the ice even in the depths of winter. The water gives them a place to stockpile food, too, Tape notes. That constant supply of liquid water also provides year-round habitat for fish, amphibians and even some insects in their larval stages. None of these species are part of the beaver’s diet, but they could serve as food for other creatures. “All that diversity would add whole new layers to food webs,” Roth says.
Ecological changes could extend well beyond the beaver pond. The water impounded by beaver dams sometimes finds its way past the dam, Tape says. The satellite photos that he and his colleagues analyzed revealed that some stretches of river just downstream of beaver dams now remain unfrozen even in winter. That flowing water probably spills over the dam or around its edges, but some may seep through or under the structure.
That liquid water also helps thaw the underlying permafrost. Previous studies have shown that even a shallow pond less than a meter deep can boost sediment temperature by as much as 10 degrees C above the locale’s average air temperature. That kind of warming causes permafrost to thaw decades earlier than it would without the pond. Although scientists are concerned that permafrost thawing will release stored carbon into the atmosphere, no one yet knows how that thawing will affect the balance of carbon emissions to the atmosphere (SN: 1/21/17, p. 15).
Field studies at lower latitudes hint that beavers will probably bring about other ecological changes, too, Tape says, which might shift over time. For example, moose and snowshoe hares eat the same willow shrubs that beavers consume and build their dams with. And ptarmigan, a crow-sized bird in the grouse family, rely on those shrubs for cover, especially during winter. So immediately after beavers move into an area and start clearing that brush, populations of those species may decline.
But the long-term benefits will probably outweigh the short-term impacts on those species, says Matthew Mumma, an ecologist at the University of Northern British Columbia in Prince George, Canada. Permafrost that thaws along the fringe of a beaver pond will probably boost numbers of the shrubs that these species depend on, Tape and colleagues suggest. So in the long run, the overall numbers of moose, hares and ptarmigan may rise.
Likewise, Mumma notes, beavers could provide big benefits for salmon and other migratory fish. Beaver dams were once thought to impede the travel of such fish upstream or to reduce the number of places where fish could spawn. But studies in the western United States, among other places, have suggested that the presence of beavers actually helps boost populations of salmon. For instance, the aquatic grasses in beaver ponds offer hiding places for young fish. Also, the languid ponds provide a resting spot for adult fish migrating upstream to spawning sites.
Better-fed wolves
Boosting herbivore populations on the tundra would be a boon for local predators, of course. Larger numbers of snowshoe hares, for example, could feed the populations of the arctic foxes that prey upon them, Mumma says. And more moose could mean better-fed wolves.
Beavers themselves make a meal for bears, wolverines and wolves. In areas where wolves and beavers coexist, the rodents make up as much as 30 percent of the wolf diet, Roth says. The presence of a more reliable and more diversified food supply could lead wolves to settle down in smaller territories rather than migrating widely.
Benson and his team have already seen the impact of beaver populations on wolves, coyotes and wolf-coyote hybrids in Ontario’s Algonquin Provincial Park from August 2002 until April 2011.
In that time, 37 of the 105 pups that had been tagged with radio transmitters died, Benson says. The second-highest cause of death was starvation. Every one of those starvation-related deaths took place in the western portion of the park, which has relatively rugged terrain and few beavers. In the eastern portion of the park, where beavers are plentiful, none of the pups starved, Benson and his team reported in 2013 in Biological Conservation.
In a separate study, Mumma and colleagues analyzed aerial surveys of beaver populations within seven broad regions in northeastern British Columbia in 2011 and 2012. Proximity to human activity, such as roadbuilding or oil and gas exploration, didn’t seem to affect beavers’ decisions to build at a particular locale. Nor did the presence of wolves in the area, the researchers reported in February in the Canadian Journal of Zoology.
Although having wolves nearby seemed to affect the number of beavers present (quite possibly via consumption), the predators didn’t seem to scare the rodents away entirely, Mumma notes.
More beavers, fewer sick moose
Whether the presence of beavers on the Alaskan tundra ends up boosting the numbers of moose and other ungulates, the dam builders could have a big, though indirect, impact on the hoofed browsers’ health.
Roth and parasitologist Olwyn Friesen, now at the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, recently studied how a wolf’s diet affects the parasites it carries — which can then be passed on to other creatures in the environment. The researchers analyzed 32 wolf carcasses collected by provincial conservation officers in southeastern Manitoba in 2011 and 2012. Those remains came from hunters, trappers and roadkill.
In particular, the team tallied the parasites in the wolves’ lungs, liver, heart and intestines. The group also measured the ratio of carbon-12 and carbon-13 isotopes in the wolf tissues, which provided insight into what sorts of prey each individual wolf had eaten near the time those tissues formed.
Typical prey for wolves in this area are, from most consumed to least: white-tailed deer, snowshoe hare, moose, beaver and caribou, Roth says. Each of these creatures has a distinct ratio of the two carbon isotopes in its tissues. That ratio gets passed along to the predators that eat them.
The wolves with diets heavier in beaver had, on average, fewer intestinal parasites called cestodes. (Tapeworms are the best-known members of that group.)
The implications are clear, Roth and Friesen reported in 2016 in the Journal of Animal Ecology. Beaver-eating wolves are much less likely to excrete parasites into the environment where they could be picked up by ungulates, such as moose and caribou. Wolves don’t seem to be detrimentally affected by such parasites. But ungulates that become infected — especially older animals — may have reduced lung capacity, making escape from predators more difficult.
A new resource
Although beavers may speed changes in the Arctic, those effects may still take a long time to manifest.
Despite the proliferation of beavers in the Lower Noatak River watershed in the last couple of decades, “things around here grow so slowly, they’re not really having a long-term impact yet,” says local resident Kirk. Shrubs haven’t yet noticeably spread into any areas of permafrost that have been thawed by waters impounded by recent dam-building.
Nor have the beavers made much of a mark on the local economy, he says. “There’s a lot of people harvesting them now, since there’s so many of them around,” he adds. However, the pelts from those rodents are so far used by the trappers themselves, not sold to others.
The beavers haven’t become a big draw on the local food scene, either. Even connoisseurs say the meat has a gamey, greasy taste. As Kirk puts it, “we haven’t adjusted our taste buds to them yet.”